RGB and CMYK are two primary color modes, which play great roles in shaping our visual experiences. RGB (Red, Green, Blue) is the foundation for digital displays, creating colors by combining light intensities of these primary hues. CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black) comes into play for print materials.
Understanding the differences between RGB and CMYK color modes is paramount for creators and designers. It ensures that the intended colors translate accurately across various mediums, from digital screens to print materials. Incorrect color mode selection can lead to unexpected color shifts, compromising the visual impact and consistency of your work. This knowledge enhances the quality and integrity of designer’s projects.
What is RGB?

RGB stands for “Red, Green, Blue”. It’s a color model used for displaying colors on electronic screens, such as computer monitors, TVs and digital devices. In the RGB model, colors are created by mixing red, green, and blue light. By adjusting the levels of these three primary colors, a wide range of colors can be produced. This color mode is commonly used for digital design, web graphics and anything that will be displayed on electronic screens.
When to use RGB
RGB is ideal for platforms where colors are displayed on screens. Use RGB in the giving platforms helps you in your works.
Digital Graphics
When creating digital graphics using software like Photoshop or Illustrator, opt for RGB. It ensures vibrant and accurate colors, maintaining their integrity when displayed on screens.
Online Content
For online content such as websites, social media posts and digital ads, RGB is the preferred choice.
Digital Art
Digital artists often use RGB color mode to create vibrant and dynamic artworks. This mode allows them to work with a wide range of colors and achieve the desired visual impact in their digital illustrations and designs.
Videos and Animations
In videos and animations, RGB is crucial for maintaining color accuracy and vibrancy across different screens. RGB color values ensure that the colors appear consistent and vibrant, enhancing the overall visual experience in videos, animations, and multimedia projects.
User Interface (UI) Design
RGB is essential for UI design as it guarantees precise color representation on digital displays. It enhances the overall design aesthetics and usability of websites, apps and software interfaces.
Screen Presentations
RGB is optimal for screen presentations, such as slideshows and digital presentations. Using RGB ensures that the colors displayed on screens match the intended design. With the vibrant visuals this color mode captivates and engages audiences during lectures, meetings and multimedia presentations.
What are the best file formats for RGB?

Some file formats are given bellow for using RGB color mode. These formats offer versatility and maintain color integrity in digital displays.
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): Well-suited for photographs due to its efficient compression, maintaining good quality. However, repeated editing can lead to quality loss.
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): PNG is a top choice for RGB color mode due to its lossless compression and transparent background support. It’s ideal for web graphics, logos, and illustrations needing high quality and transparency.
- GIF (Graphics Interchange Format): Commonly used for animations and simple images with limited colors. It supports transparency but has limited color depth.
- WebP: Google’s modern format, offering both lossless and lossy compression. It delivers high-quality images with smaller file sizes, making it perfect for web use.
- SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics): SVG is a versatile file format suitable for RGB color mode because it’s based on vector graphics. This means it can represent images using mathematical equations, allowing them to be infinitely scalable without losing quality.
What is CMYK?

CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black). It’s a color model used in color printing, where different percentages of these four colors are combined to create a wide range of colors. CMYK is primarily used for print materials, such as magazines, brochures and posters.
When to use CMYK
CMYK color mode is best for printing processes. Let’s explore some essential sectors to use this color mode,
- Print Materials: CMYK is essential when designing materials intended for physical printing, such as brochures, flyers, business cards and posters. It ensures that the colors will be accurately reproduced on the final printed products.
- Professional Printing: CMYK is the standard color mode for professional printing processes, including offset and digital printing.
- Consistent Branding: When it comes to branding materials, such as logos, corporate colors and marketing collateral, using CMYK ensures that the colors remain consistent across various printed items. This consistency is essential for building a strong brand identity.
- Color-Critical Designs: If your design relies heavily on precise color reproduction, such as in photography, artwork, or illustrations, using CMYK is recommended.
- High-Quality Prints: CMYK printing produces high-quality prints with fine details. It is suitable for projects that demand professional-level results, like magazines, art prints and high-end promotional materials.
- Photographic Prints: CMYK is preferred for reproducing photographic images in print. It ensures that the subtleties of color, tone and detail are accurately translated from the digital image to the physical print.
What are the best file formats for CMYK?

There are some specific file formats which are appropriate for using CMYK. Certain formats among them are discussed here:
- PDF (Portable Document Format): PDF is a versatile format suitable for sharing documents that include text, images and graphics. It preserves CMYK colors and ensures consistent printing across different systems.
- EPS (Encapsulated PostScript): EPS is a widely used vector format for CMYK graphics. It’s ideal for logos, illustrations and other designs that require high-quality printing and scalability.
- INDD (Adobe InDesign): INDD files are created in Adobe InDesign and are well-suited for designing layouts of books, magazines, brochures and other print materials that require precise control over typography and graphics.
- PSB (Photoshop Large Document Format): PSB is an extension of the PSD format, optimized for large designs. It’s suitable for CMYK images with multiple layers and high resolution, commonly used for large-scale printing.
Major differences between RGB and CMYK
| Aspect | RGB Color Mode | CMYK Color Mode |
| Full Form | Red, Green, Blue | Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key (Black) |
| Primary Colors | Uses additive primary colors | Uses subtractive primary colors |
| Color Model | Additive color model | Subtractive color model |
| Usage | Digital displays, screens, web, electronic media | Print materials, commercial printing |
| Output Devices | Monitors, TVs, cameras, scanners, digital devices | Printers, magazines, brochures, signage |
| Color Mixing | Colors are added together to create new colors | Colors are subtracted to create new colors |
| File Formats | Commonly used in JPEG, PNG, GIF, etc. formats | Commonly used in TIFF, PDF, EPS formats |
| Print Quality | Limited print quality compared to CMYK | Better print quality and color accuracy |
Which Color Mode Is Best Between RGB and CMYK?
The choice between RGB and CMYK depends on the intended use of your design. If you’re creating content for digital displays, websites and screens, RGB is the preferred color mode due to its wider range of colors. On the other hand, if your design will be printed, especially for professional printing and accurate color representation, CMYK is the better choice. It’s essential to understand the differences and purpose of each color mode to ensure your designs appear as intended across various mediums.
How to convert between RGB and CMYK
Converting between RGB and CMYK color modes is a fundamental aspect of graphic design and printing preparation. Here’s how you can do it in popular design software:
How To Change Color Mode in Photoshop:
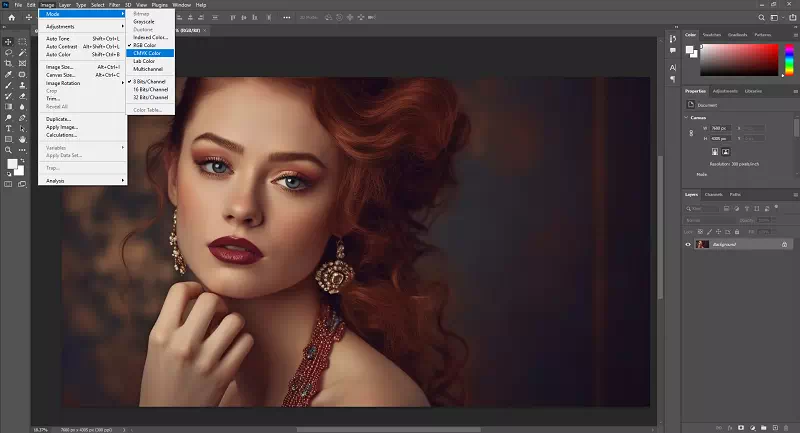
1) Open your image or design in Photoshop.
2) Go to the “Image” menu at the top.
3) Select “Mode” and choose either “RGB Color” or “CMYK Color” based on your desired color mode.
4) A confirmation dialog may appear; click “OK” to convert the color mode.
How To Change Color Mode in Illustrator:
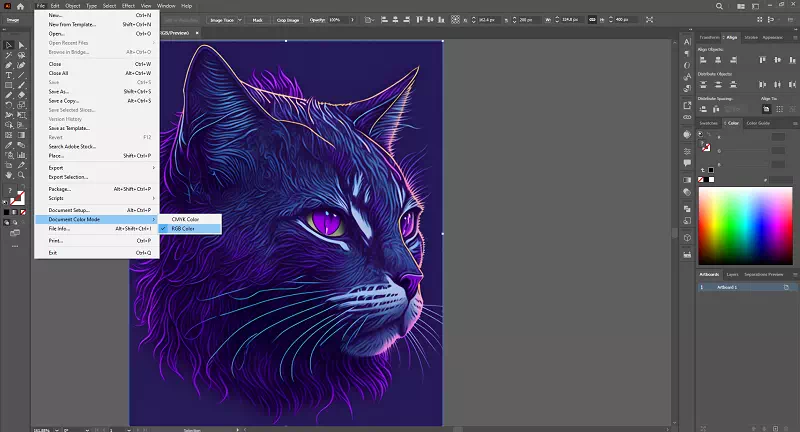
1) Open your artwork in Adobe Illustrator.
2) Navigate to the “File” menu.
3) Choose “Document Color Mode” and select either “RGB” or “CMYK” from the dropdown menu.
4) Illustrator will ask if you want to convert the colors; click “OK” to proceed.
How To Change Color Mode in InDesign
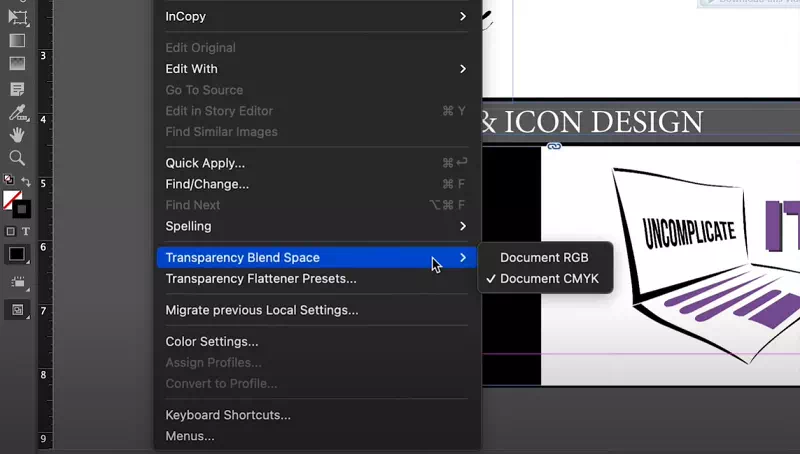
1) Open your document in Adobe InDesign.
2) Go to the “File” menu.
3) Select “Document Setup” and then choose “Intent” from the dropdown menu.
4) Choose either “Web” (for RGB) or “Print” (for CMYK) from the “Intent” options.
5) Confirm your choice by clicking “OK.”
Conclusion
RGB is ideal for digital displays, offering vibrant and wider color ranges. CMYK is designed for print, providing accurate color reproduction through ink combinations. RGB uses additive color mixing, while CMYK employs subtractive color mixing. Understanding the distinctions between RGB and CMYK color modes is very important for every designer. By understanding when to use each color mode and how to convert between them, you can create visuals that truly shine, whether on-screen or in print.
Related









